Vectors
- tags:Math
-
Cross product
- The vector product of two vectors A,B is given by AxB, and the resultant vector is perpendicular to both A and B. The product of their magnitude gives the area of the polygon which is the magnitude of the resultant vector. Its a 3-dimensional vector with the direction given by the right-hand rule, with the thumb giving the direction of the resultant.

-
A × B = A B sin θ
The vecotrs a and b form a parallelogram and the area of the parallelogram is the base time height
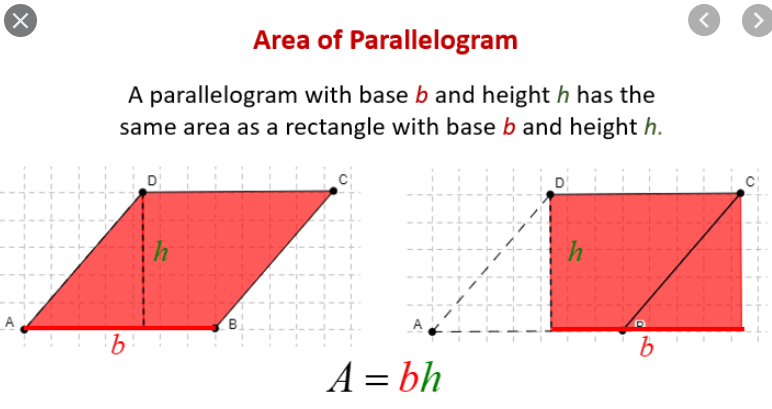 The heigh is given by the sin of the angle between vectors = asin(angle)
- The cross product of perpendicular vectors is the same as the product of magnitude as sin90 is 1. The cross product of parallel vectors is zero.
- AxB != BxA as it flips the direction of the resultant vector.
-
The heigh is given by the sin of the angle between vectors = asin(angle)
- The cross product of perpendicular vectors is the same as the product of magnitude as sin90 is 1. The cross product of parallel vectors is zero.
- AxB != BxA as it flips the direction of the resultant vector.
-  - We know that the standard basis vectors i, j, and k satisfy the below-given equalities. i × j = k and j × i = –k
j × k = i and k × j = –i
k × i = j and i × k = –j
Also, the anti-commutativity of the cross product and the distinct absence of linear independence of these vectors signifies that:
i × i = j × j = k × k = 0
-
- We know that the standard basis vectors i, j, and k satisfy the below-given equalities. i × j = k and j × i = –k
j × k = i and k × j = –i
k × i = j and i × k = –j
Also, the anti-commutativity of the cross product and the distinct absence of linear independence of these vectors signifies that:
i × i = j × j = k × k = 0
-  -
-